Residential solar power installation is revolutionizing the way homeowners think about energy and savings. Imagine harnessing the sun’s rays to not only cut down on your electricity bills but also boost your property’s value! With rising environmental concerns and financial incentives, diving into solar energy has never been more appealing. Let’s explore how making this switch can lead to both personal and planetary benefits.
From the financial perks of reduced utility costs to the satisfaction of lowering your carbon footprint, installing solar panels at home can be a game changer. We’ll break down the straightforward steps to get your solar system up and running, along with the various incentives that can lighten the load on your wallet. After all, investing in solar isn’t just about saving money—it’s about making a positive impact on the environment.
Benefits of Residential Solar Power Installation
Residential solar power installation offers a multitude of advantages that can significantly enhance both financial and environmental aspects of homeownership. As more homeowners look to green energy solutions, understanding these benefits becomes essential not only for personal savings but also for contributing to a sustainable future.
One of the most compelling reasons to consider installing solar panels is the financial advantage they provide. By harnessing the power of the sun, homeowners can drastically reduce their electricity bills. In many cases, solar panels can offset a large percentage of a household’s energy usage, leading to savings that can amount to hundreds or even thousands of dollars annually. Additionally, many states offer tax incentives, rebates, and solar renewable energy credits, which further decrease the initial investment cost. Over time, these savings can lead to a complete return on investment, making solar a financially sound choice.
Financial Advantages of Installing Solar Panels
Installing solar panels can lead to substantial financial benefits. It’s crucial to understand the specific ways these savings materialize:
- Reduction in Electricity Bills: Many homeowners experience a significant decrease in their monthly utility bills. Depending on local energy rates and the size of the solar system, some can eliminate their power bills entirely.
- Tax Credits and Incentives: The federal solar tax credit allows homeowners to deduct a percentage of the installation costs from their federal taxes, enhancing the financial attractiveness of solar power.
- Low Maintenance Costs: Solar panels require minimal maintenance, often needing only periodic cleaning and an occasional inspection, which helps keep costs low in the long run.
- Long-term Investment Value: Solar installations are durable, often lasting 25 years or more, making them a long-term investment that pays off significantly over time.
Environmental Benefits of Reducing Carbon Footprint
The switch to solar energy significantly impacts the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The energy that comes from solar panels is clean and renewable, which is vital for combating climate change.
- Reduced Carbon Emissions: By generating energy from the sun, homeowners can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels, thereby decreasing their carbon footprint. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, the average residential solar system can offset roughly 3 to 4 tons of carbon emissions annually, equivalent to planting over 100 trees each year.
- Conservation of Resources: Solar energy harnesses an abundant natural resource, minimizing the depletion of finite resources like coal, oil, and natural gas.
- Improved Air Quality: As solar energy reduces reliance on traditional power plants, it helps mitigate air pollution, leading to healthier communities.
Increased Property Value and Marketability
Investing in solar power can enhance your home’s value and attractiveness in the real estate market.
- Higher Resale Value: Homes equipped with solar energy systems can see an increase in market value. Studies have shown that solar panels can increase a property’s resale value by an average of $15,000.
- Attracting Eco-Conscious Buyers: As more people prioritize sustainability, homes with solar installations appeal to buyers looking for energy-efficient features.
- Market Differentiation: A solar-equipped home stands out in a competitive market, making it easier to sell compared to traditional homes without solar systems.
The investment in solar energy not only benefits the homeowner but also contributes to a healthier planet for future generations.
Steps to Install Residential Solar Power Systems

Installing solar panels on your home can feel like a daunting task, but breaking it down into manageable steps makes it much easier. By following a structured approach, you can ensure that you’re making informed decisions that will optimize your energy savings and enhance the value of your home. Here’s a straightforward guide to help you navigate the process of installing a solar power system at your residence.
Assessing Your Home for Solar Panel Installation
Before diving into the installation process, it’s crucial to evaluate whether your home is suitable for solar panel installation. This assessment involves several key considerations, including roof orientation, shading, and overall energy needs.
- Roof Orientation and Condition: The direction your roof faces has a significant impact on solar efficiency. South-facing roofs typically receive the most sunlight throughout the day. It’s also essential to check if your roof is in good condition; any repairs should be made before installation.
- Shading Analysis: Evaluate any potential shading from trees, buildings, or other structures that could hinder sunlight exposure. Tools such as solar pathfinders can help determine how sunlight travels across your property.
- Energy Consumption: Review your current electricity bills to understand your energy needs. This insight will help in determining the size of the solar system you’ll require to meet your consumption.
Choosing the Right Solar Technology and Equipment
Selecting the appropriate solar technology is critical to maximizing the benefits of your solar power system. Various types of solar panels and technologies exist, each with its own advantages.
- Solar Panel Types: There are generally three types of solar panels: monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film. Monocrystalline panels are highly efficient and space-saving, while polycrystalline panels are more affordable but slightly less efficient. Thin-film panels are lightweight and flexible but typically require more space.
- Inverters: The inverter converts the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity, which is used in homes. Options include string inverters, microinverters, and power optimizers. Each option has its benefits depending on your system layout and shading conditions.
- Battery Storage: If you want to maximize energy independence, consider adding a battery storage system. This allows you to store excess energy generated during the day for use during nighttime or power outages.
Timeline and Key Milestones for Solar Installation Projects, Residential solar power installation
Understanding the timeline for your solar installation project can help you manage expectations and plan accordingly. A typical solar installation project includes various stages, each with its own milestones.
- Initial Consultation (1-2 Weeks): This phase involves meeting with a solar consultant who will assess your property and provide you with an estimate based on your energy needs and the condition of your roof.
- Design and Permitting (2-6 Weeks): After the initial consultation, the solar company will design your system and submit the necessary permits to local authorities. This step may vary depending on local regulations.
- Installation (1-3 Days): Once all permits are approved, the installation team will set up the solar panels, inverter, and any additional equipment. The actual installation typically takes just a few days.
- Inspection and Interconnection (1-4 Weeks): After installation, your system must pass an inspection by your local building department. Following this, you’ll coordinate with your utility company to connect your solar system to the grid.
- Activation (1 Day): After passing inspection and interconnection, you can finally activate your system and start enjoying the benefits of solar energy!
“Taking the time to properly assess your home’s suitability for solar and choosing the right equipment can significantly affect the performance and longevity of your solar power system.”
Incentives and Financing Options for Solar Installation: Residential Solar Power Installation
Investing in residential solar power can seem daunting, but various incentives and financing options make it more accessible and financially viable for homeowners. Understanding these elements can lead to significant savings and a more sustainable lifestyle.
Government incentives and tax credits provide homeowners with an opportunity to reduce the upfront costs associated with solar installation. The federal government offers the Investment Tax Credit (ITC), which allows homeowners to deduct a percentage of their solar installation costs from their federal taxes. As of 2023, this credit remains at 30% of the total system cost, significantly reducing the financial burden on homeowners looking to adopt solar energy. Additionally, many states and local municipalities provide their own incentives, such as rebates and grants, which can further lower costs.
Government Incentives and Tax Credits
The landscape of government incentives for solar power is rich and varied, helping to encourage the adoption of clean energy. Here are some key incentives available to homeowners:
- Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC): Allows homeowners to deduct 30% of the cost of their solar system from their federal taxes.
- State Tax Credits: Some states offer additional tax credits that can be combined with the ITC for even greater savings.
- Cash Rebates: Many local utilities provide cash rebates for installing solar systems, which can result in immediate savings.
- Net Metering: Homeowners can sell excess energy back to the grid, often at retail rates, providing an additional revenue stream.
- Sales Tax Exemptions: Some states exempt solar systems from sales tax, further reducing upfront costs.
Financing options are crucial for homeowners looking to install solar systems, as they can help spread the initial investment over time. Homeowners can choose between several financing methods to best suit their financial situations.
Financing Options for Solar Installation
When considering the financial aspects of solar energy installation, homeowners have several financing options to evaluate. Each option has its specific advantages and drawbacks, making it essential to choose based on personal financial goals.
- Solar Loans: These are personal or home equity loans specifically designed for solar installations. They allow homeowners to own their solar system outright while paying off the loan over time, usually with lower interest rates than other types of loans.
- Solar Leases: Homeowners can lease a solar system for a set period, typically 20 years, paying a monthly fee for using the system without any upfront cost. However, they don’t own the system and may not benefit from tax credits.
- Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): Similar to leasing, homeowners pay for the electricity generated by the solar system at a predetermined rate, which is often lower than their local utility rates. This option also usually requires no upfront costs.
The long-term financial implications of investing in residential solar power can be profound. Homeowners not only save on energy bills but also potentially increase their property values.
Long-term Financial Implications
Investing in solar energy has several long-term financial benefits that can make it an attractive option for homeowners.
“A solar installation can increase home value by an average of 4.1%.” – National Renewable Energy Laboratory
Over time, the savings on electricity bills can lead to substantial financial gain. For instance, if a homeowner spends $100 a month on electricity, that amounts to $1,200 annually. With an average solar system cost of around $20,000, the investment can pay for itself in as little as 5 to 7 years through savings on electricity bills, depending on local energy costs and incentives.
Moreover, as utility companies continue to raise rates, solar systems become an even more valuable asset, shielding homeowners from future price hikes. Additionally, with the ITC and other incentives, the initial investment can be significantly reduced, further enhancing the attractiveness of solar power as a long-term financial strategy.
Maintenance and Performance of Solar Power Systems
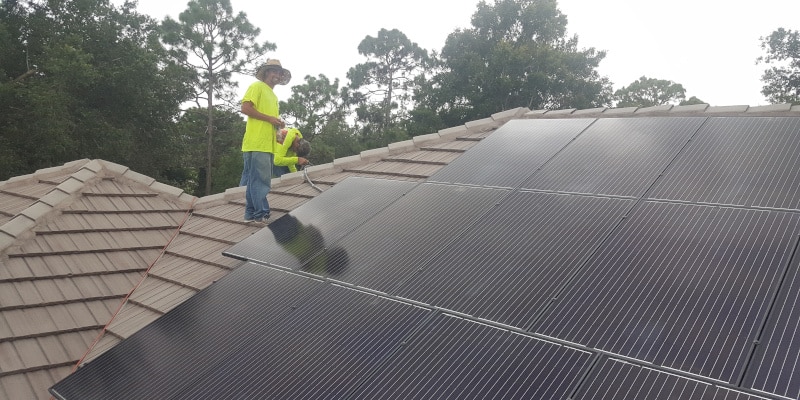

Routine maintenance is essential for ensuring that residential solar power systems operate efficiently and effectively. Just like any other technology, solar panels require care and attention to maintain optimal performance over their lifespan. The following sections will cover the necessary maintenance tasks, best practices for monitoring system performance, and common issues that homeowners may encounter.
Routine Maintenance Tasks
Regular maintenance of solar panels is crucial for maximizing their energy production and extending their lifespan. Homeowners should carry out the following tasks:
- Cleaning the Solar Panels: Dust, dirt, leaves, and bird droppings can accumulate on solar panels and block sunlight. A gentle cleaning with water and a soft brush or sponge is usually sufficient. In areas with high dust or pollen, more frequent cleanings may be necessary.
- Inspecting the System: Periodically check the solar panels for any visible damage, such as cracks or chips. It’s also important to examine the mounting hardware and wiring for signs of wear or corrosion.
- Checking Inverters: Inverters convert the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity for use in homes. Ensure that the inverter is functioning properly by checking its display for any error codes or warning lights.
- Monitoring Production: Regularly review the energy production data from your solar system. Most systems come with monitoring software that tracks performance metrics, allowing homeowners to spot any significant drops in energy output.
Best Practices for Monitoring Solar Energy Production
Monitoring the performance of solar energy systems is vital for identifying and resolving issues early on. Here are some best practices to keep in mind:
- Use Monitoring Software: Modern solar systems often come with built-in monitoring tools or apps. These allow homeowners to track energy production in real-time, enabling quick responses to any performance issues.
- Set Performance Benchmarks: Understand the expected energy output based on the system size and local weather conditions. This helps in recognizing when performance drops below expected levels.
- Schedule Regular Check-Ins: Establish a routine—whether monthly or quarterly—to assess production data and potential anomalies. During these check-ins, consider comparing your production data with historical data to spot trends.
Common Issues and Solutions
While residential solar installations are generally reliable, certain issues may arise. Being aware of these common challenges can help homeowners address them promptly:
- Shading Problems: Trees or buildings can create shade, reducing energy production. To mitigate this, consider trimming overhanging branches or installing solar panels in a less shaded area.
- Inverter Failures: Inverters can fail due to wear over time. If the inverter shows error codes or stops working, consult a professional to repair or replace it as needed.
- Electrical Connections: Loose or corroded electrical connections can lead to performance issues or even safety hazards. Regular inspections can help identify and fix these before they become serious problems.
- Panel Degradation: Over time, solar panels may experience degradation in efficiency. Most panels come with a warranty that guarantees a specific level of performance over 25 years; if performance drops significantly, consult the manufacturer.
If you’re thinking about going solar, it’s crucial to understand the cost to put solar on house. These expenses can vary based on factors like location and system size. Once you have a grasp on that, you might also want to check out the cost of sunrun solar panels , which could influence your decision significantly and help you budget wisely for your solar project.
If you’re considering installing solar panels, it’s important to know the cost to put solar on house. This price can vary depending on factors like location and system size. Understanding these costs can help you budget better. Additionally, if you’re looking at specific brands, check out the cost of sunrun solar panels for a clearer picture of your investment options.
When thinking about solar energy, the cost of sunrun solar panels is a key factor to consider. These panels can be a great choice for homeowners looking to save on energy bills. Coupled with the cost to put solar on house , it’s essential to do your research to ensure you’re making a smart investment for the long term.